Welcome to Financial Planning. The Overview section covers:
- Introduction - Read about Clarizen Financial Planning capabilities
- Concepts and Data Fields Used in Financial Planning - Understand financial terminology, calculations, top-down vs bottom-up planning, labor and non-labor resources (NLR), and more.
- Getting Started - For administrators, learn how to enable and set up Financial Planning. For Project Managers and Controllers, learn how to set up project financials and track your financials.
Introduction
Plan, manage and track your project financials using Financial Planning in Clarizen. Financial Planning provides a fast, simple, and familiar way of working with project budgets that combines the simplicity of a spreadsheet for data entry, with the control and structure that organizations need to keep track of the bigger picture, at scale, and over time.
Financial Planning includes standard features for Capex/Opex spend planning and Revenue Forecasting and tracking for Billable projects.
Tracking actual costs and revenues is frequently done with a counterpart Project Controller in a Finance or Operations team and may involve setting up an integration with an external financials or ERP system like SAP or Oracle.
Financial Planning views offer time-phased planning capabilities with a financial dimension for estimating and controlling projects.
Financial Planning lets you capture Non-Labor Resource (NLR) costs and revenues. NLRs can include any materials, equipment, infrastructure or other costs that impact the overall cost and revenue of your project.
Financial Planning views allow for adding Non-Labor Resources to a Project and setting Budget plan, Forecast and Actual amounts for Costs & Revenues per time period. Amounts are summarized by NLR and period (e.g. Travel costs, by financial quarter). Total aggregate amounts are rolled up to the project and incorporated in the Budgeted & Actual Cost, Expected & Actual Revenue as well as other standard Clarizen financial KPIs including Year to Date Actuals, Financial Year Forecasts.
All data in Financial Planning views can be reported on in Reports using the Projects > Financial Resources special collection which combines all Labor and Non-Labor data including all data about the resources (e.g. categories, job titles) and financial month time phase data.
Features of Financial Planning include:
- Project cost estimation (initial costing/pricing)
- Project cost budgeting (detailed budget with work plan)
- Project cost control (monthly tracking of actuals)
- Project revenue forecasting (month, quarter, year)
- Revenue recognition for time & materials projects (revenue actuals)
Financial Planning can also be used as an input for:
- Project procurement plans (coordinating purchasing plans)
- Project funding requests (FQ or FY Capex/Opex planning)
- Professional services account planning and revenue forecasts
- Revenue Recognition
Depending on your requirements, you can use Financial Planning for different workflows:
High-Level Budget Estimate

Detailed Budget Planning

Tracking Monthly Actuals

Cross-Project Financial Reporting

Concepts and Data Fields Used in Financial Planning
Learn about financial concepts and how they are used for Financial Planning in Clarizen.
These are the anchor fields of Financial Plans for your projects in Clarizen.
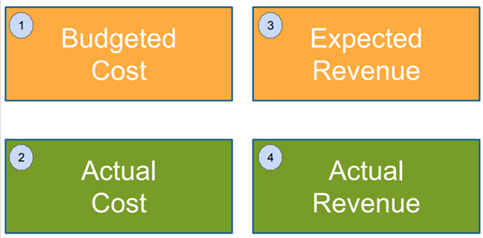
Balancing these will help you plan for profitability and manage against plans.
Note: If you’re not running billable projects, use Expected Revenue to capture monetary benefits. You can rename the fields to suit your organization's terminology.
Standard Work Item Fields for Budget Management
The table below describes the fields used in Clarizen for Financial Planning and include manually-entered fields and calculated (‘formula-based’) KPIs.
The Fundamental Four (highlighted) may be manually set, but otherwise will be calculated based on hourly rates.
|
Field |
Definition |
From Financial Plan |
Can be Manually Set |
Formula-Based |
|
Budgeted Amount |
A top-down budget amount total. The amount allocated to the Project. |
|
✓ |
|
|
Budgeted Cost |
A rolling-up cost field. Also known as Budget at Completion. (Planned Work * Hourly Cost Rates) + Non-Labor Budget Costs |
✓ |
✓ |
|
|
Budget Variance |
Budgeted Amount - Budgeted Cost |
|
|
✓ |
|
Actual Cost |
Work Item progress + Non-Labor Actual Costs |
✓ |
✓ |
|
|
% Invested |
(Actual Cost / Budgeted Cost) % |
|
|
✓ |
|
Expected Revenue |
(Planned Work * Hourly Billing Rates) + Billable Non-Labor Budget Revenue |
✓ |
✓ |
|
|
Actual Revenue |
Timesheets Duration * Hourly Billing Rates) + Billable Non-Labor Actual Revenue + Actual Billed Expenses |
✓ |
✓ |
|
|
Remaining Budget |
Budgeted Amount - Actual Cost |
|
|
✓ |
|
Cost Balance |
Budgeted Cost - Actual Cost |
|
|
✓ |
|
CPI |
Cost Performance Index. Earned Value / Actual Costs |
|
|
✓ |
|
SPI |
Schedule Performance Index. Earned Value / Planned Value |
|
|
✓ |
|
Planned Value |
Expected Progress * Budgeted Cost. This is not displayed but is calculated on a daily basis. |
|
|
✓ |
|
Expected Progress |
A linear projection of a task’s work distributed over that task’s duration as defined in the Work Plan. It’s affected if you update the Work or the Duration. When assigned to a resource, the work is assigned to that resource’s work load according to that person’s availability (working hours and time off). This is the task’s Resource Load. Example: Project 1 has 2 tasks: Task A is an 8 hour task. And has one resource (let’s call him “Bob”). Bob has an 8 hour work day and full availability to take on new project work, so we expect Bob to complete the task in one day. Task B is a 3 day task. It has a dependency on task A, so that it is scheduled to start only after A is complete. Again it has only one person, Bob, assigned to do the work. As Clarizen only takes into account working hours, the 3 day task with a single resource is the equivalent of 24 person/hours of work (that is: 8h * 3 = 24h). |
|
|
✓ |
|
Earned Value |
Budgeted Cost of Work Performed (BCWP). Completed Work expressed in terms of the Budgeted Cost. |
|
|
✓ |
|
Cost Variance |
Earned value - Actual Cost |
|
|
✓ |
|
ETC |
(Budgeted Cost - EV)/(CPI*SPI). A forecast of how much more money will need to be spent to complete the project. |
|
|
✓ |
|
EAC |
Estimate at Complete = Actual Cost + Estimate to Complete |
|
|
✓ |
|
Budget Net Revenue |
Budget Net Revenue = Budget Labor Revenue + Budget Revenue of BILLABLE 'internal' Non-Labor Resources + Planned Profit of 3rd Party Non-Labor Resources |
|
|
|
| Planned Net Margin % |
(Planned Profit / Budget Net Revenue) * 100 |
|
|
|
| Suggested Revenue |
When Project's Labor Budget = Task Assignment, uses Work x Rates. When Project's Labor Budget = Project Assignment, uses Project Assignment x Rates"" AND Budget Revenue from Non-Labor Resources. |
|
|
|
| Actual Net Revenue |
Actual Revenue of billable 'internal' Non-Labor Resources AND Actual Profit of billable 3rd Party Non-Labor Resources AND (Actual Effort x Rates). See note below table |
|
|
|
| Actual Contribution % |
(Actual Profit / Actual Net Revenue) * 100 |
|
|
|
| Revenue EV |
Labor = Actual Effort * Rates. Non-labor = actual margin of billable non labor |
|
|
|
| Suggested Net Revenue |
When Project's Labor Budget = Task Assignment, uses Work x Rates. When Project's Labor Budget = Project Assignment, uses Project Assignment x Rates. For Non-Labor, Planned Profit of billable of 3rd Party Non Labor Resources, else Budget Revenue |
|
|
|
| Suggested Actual Net Revenue |
Suggested Actual Net Revenue = Suggested Actual Labor Revenue + Actual Revenue of internal Non-Labor Resources + Actual Profit of 3rd Party Non-Labor Resources |
|
|
|
Actual Net Revenue calculations
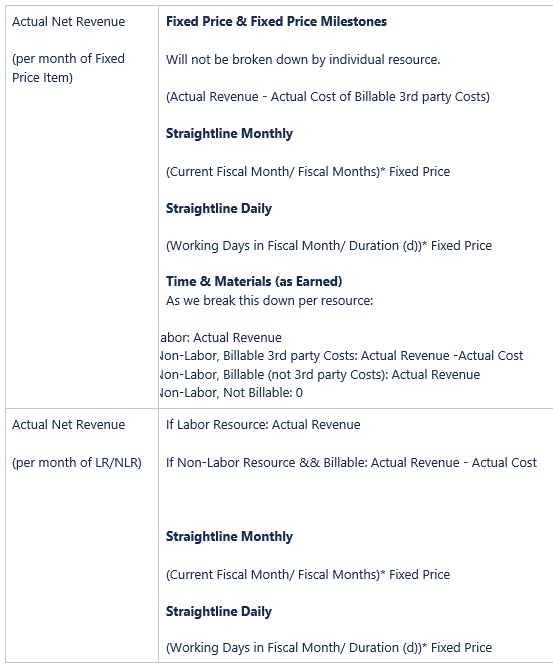
For time-phased planning, there are forecasting fields that allow intra-month manual tracking of forecasted amounts that do not alter your work plans.
|
Financial Planning Fields |
Definition |
From Financial Plan |
Can be Manually Set |
Formula-Based |
|
Budget Cost |
Rolls up to Work Item Budgeted Cost. Labor Costs are calculated from Resource Planning * Cost Rates |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
|
Actual Cost |
Rolls up to Work Item Actual Cost. Labor Actuals are calculated from Timesheets. |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
|
Forecast Cost |
Manually set, does not roll up to work item. |
✓ |
✓ |
|
|
Budget Revenue |
Rolls up to Work Item Expected Revenue. Labor Revenues are calculated from Resource Planning * Billing Rates |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
|
Actual Revenue |
Rolls up to Work Item Actual Revenue. Labor Actuals are calculated from Timesheets. |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
|
Forecast Revenue |
Manually set, does not roll up to work item. |
✓ |
✓ |
Labor and Non-Labor Resources have an Expense Type field (Capex and Opex) to be used with the following fields:
|
PLAN |
ACTUAL |
|
Budget Cost Opex
|
Actual Cost Opex
|
|
Budget Cost Capex
|
Actual Cost Capex
|
|
Budget Cost Labor
|
Actual Cost Labor
|
|
Budget Cost Non-Labor
|
Actual Cost Non-Labor
|
Top Down and Bottom Up Planning
Depending on how you work, the methods below will define how you work with Financial Planning.
Top-Down
- Budgeted Amount - A top-down currency amount, not time-phased. Use this to record the total contract amount or funding amount of a Project.
- Budgeted Work - A top-down duration amount, not time-phased. Use this to record total sold hours. Does not drive any calculations.
Bottom-Up
- Work - A roll-up duration amount reflecting planned effort. Can be time-phased with Resource Planning.
- Budgeted Cost - A roll-up duration amount reflecting the planned effort * hourly rates. Can be time-phased with Financial Planning.
Track the Amount between what was budgeted (sold) vs your work plan costs with:
Budget Variance = Budgeted Amount – Budgeted Cost (“Contingency” or “Buffer”)
Fixed Cost and Fixed Price Items
All Work Items in Clarizen can have a Fixed Cost or Fixed Price that overrides Budgeted Cost and Expected Revenue respectively.
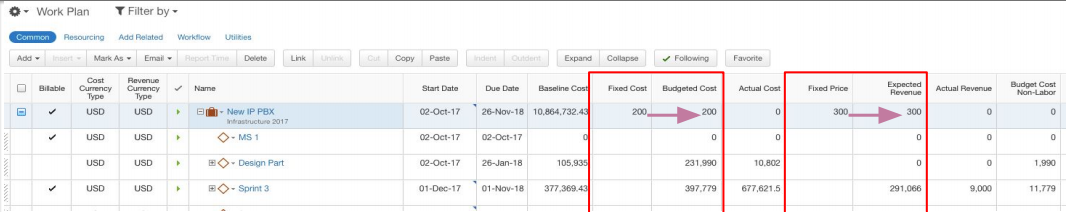
Limitations
- Fixed Cost, Manually-Set: Budgeted Cost, Expected Revenue, Actual Cost & Actual Revenue amounts set on work items can not be time-phased and are not displayed in the Financial Planning view. Amounts cannot be divided into Labor/Non-Labor and Capex/Opex.
- Work Item Direct Planned Expenses & Direct Planned Billed Expenses are not time-phased and are not displayed in the Financial Planning view. Amounts cannot be divided into Labor/Non-Labor and Capex/Opex.
Best Practices
- Fixed Price and Fixed Price Milestone projects and can be managed using the Billing Type field - read more about Billing Types
- Unless you are setting the Fixed Costs & Direct Planned Expenses via an integration (for example, Salesforce), plan to retire these fields, remove them from profiles and layouts and migrate users to the more accurate Financial Planning.
- Use Non-Labor to capture time-phased budget (plan) and actual amounts.
- Use Validation rules to prevent manually-set Budgeted & Actual cost values that block time-phasing.
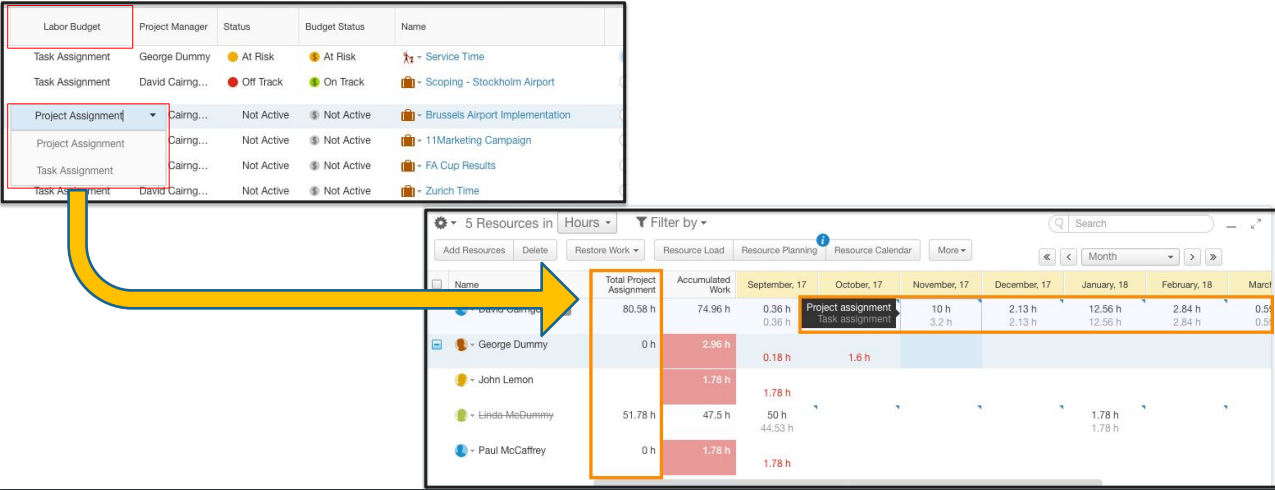
Labor Budget: Standard Rates and Labor Calculation
A Project’s Labor Budget setting offers an additional option for Labor Budget Costing:
- Task Assignment will calculate Labor Budget based on Work * User Hourly Rates
- Project Assignment will calculate Labor Budget based on Total Project Assignment * User Rates
Non-Labor Resources (NLRs)
Non-Labor Resources lets you maintain consistency of common project non-labor resources across the organization. At this point, NLRs do not contain cost or pricing information, though these can be easily added with custom fields, as needed.
Categorization of project costs as Capital Expense (Capex) varies by industry and jurisdiction.
Generally, only internal projects can be capitalized. Consult your Finance team to verify.
Default Categories
- Hardware
- Software
- External Consultant
- Materials
- Travel
- Other
NLRs can be defined on the organization level and managed in Work Item lists as well as from within the Financial Planning view.
Getting Started
Administrators
As an administrator, you must enable and set up some system settings in Clarizen. See Setting Up Financial Planning.
Project Managers and Project Controllers
Plan and track your financials. See Working with Financial Planning.
Comments